Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plant
The main objectives of residential, commercial, and industrial wastewater treatment plants are (i) reducing water pollution and (ii) making use of the waste resulting from treatment processes to ensure a more sustainable use of water resources.
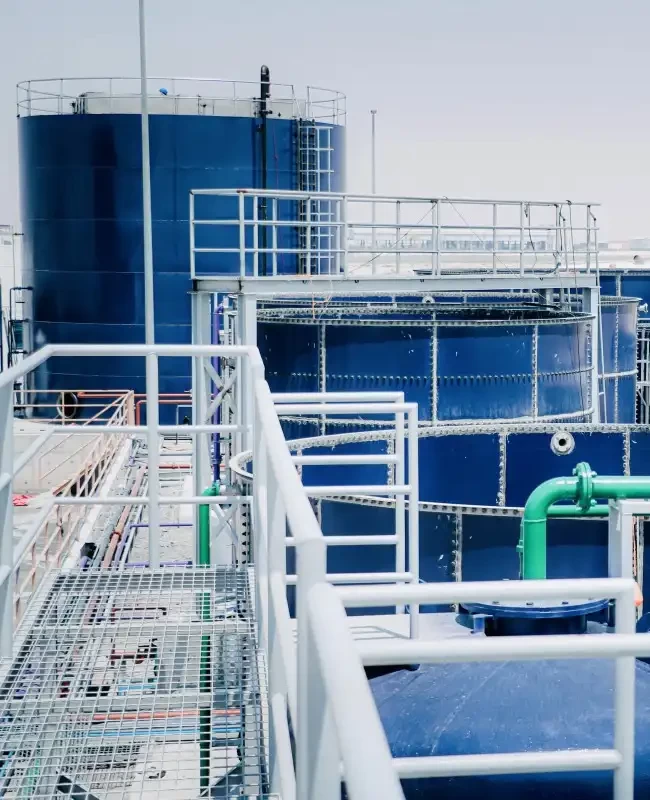
A wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) receives and treats municipal and industrial wastewater. That is, a industrial wastewater treatment plants in Kerala, India UAE and Oman treats water to remove waste, grease and floating oils, sand and any coarse debris present in the water; the wastewater treatments remove organic and inorganic materials through settling processes, as well as biodegradable organic materials dissolved in the water.
- Preliminary treatment: Preliminary wastewater treatment plants involve the separation of large solids (bottles, fabric, plastics) found in the water using bar racks and screens.
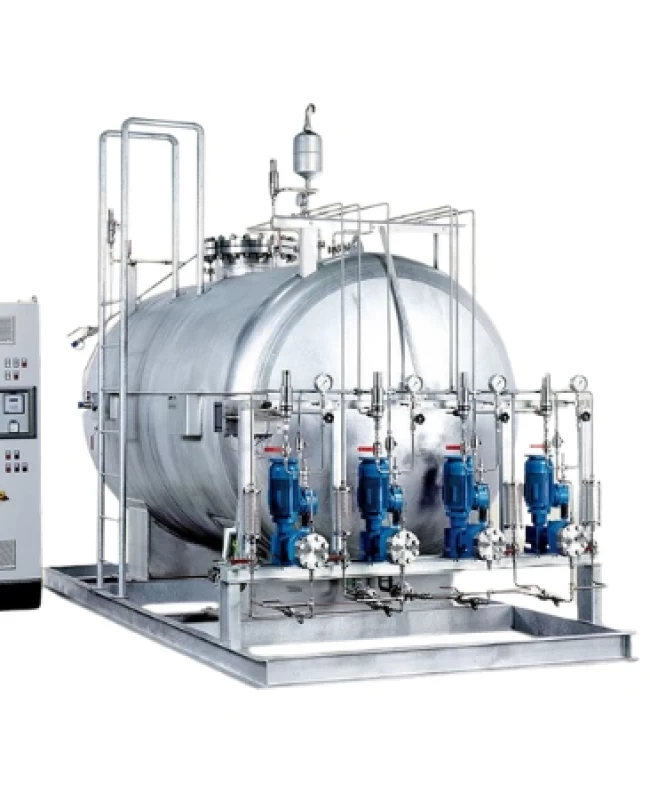
- Primary treatment: physico-chemical treatments to sediment and precipitate suspended solids and reduce the biochemical oxygen demand of the organic solids. In addition, the wastewater treatment neutralises the water, eliminates volatile contaminants, removes greases and oils, etc.
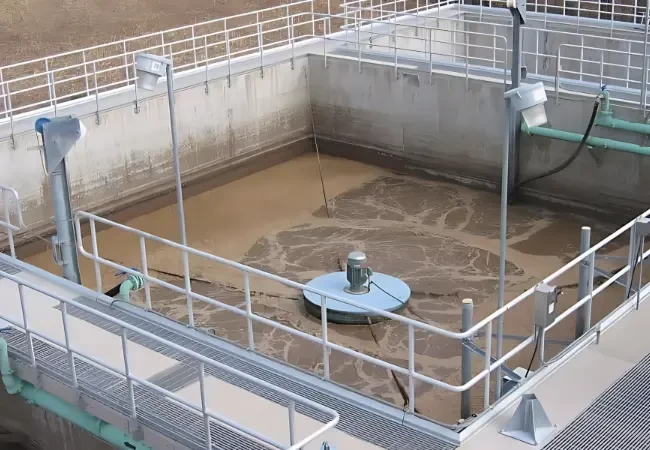
- Secondary treatment: biological treatments that reduce the amount of organic matter in wastewater. They include aerobic processes which degrade organic material in the presence of oxygen, as well as anaerobic processes which oxidise organic matter without oxygen, followed by secondary settling.
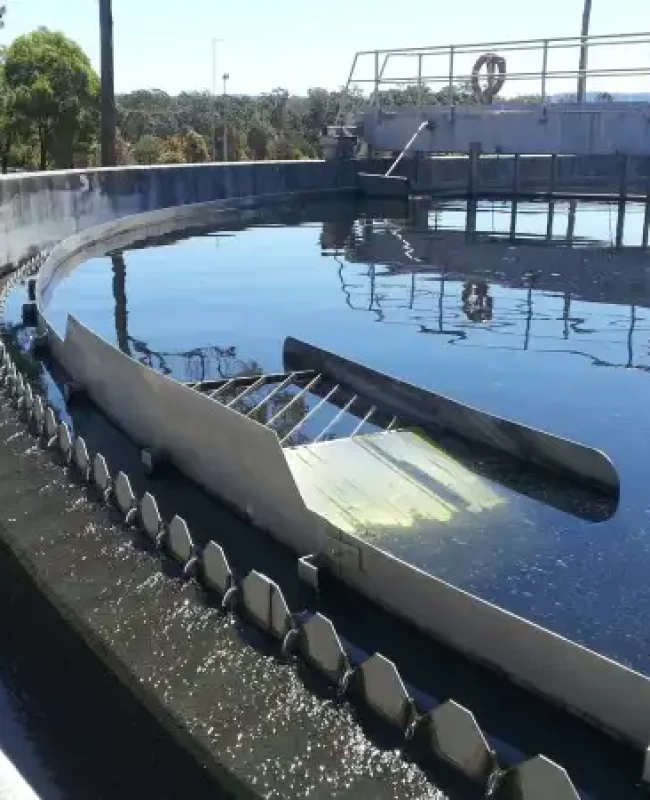
- Tertiary treatment: advanced physical, chemical and biological processes, which eliminate heavy metals, nitrogen, phosphorous, and pathogens. In some wastewater treatment plants, the water undergoes further treatment to allow its reuse for purposes such as irrigation of parks and green areas, street washing, or industrial uses.
Wastewater Treatment Plants Benefits and Goals:
- Pollution Reduction: Minimizes the impact of wastewater on natural water bodies by removing pollutants.
- Resource Sustainability: Facilitates the recycling and reuse of treated water, contributing to sustainable water resource management.
- Environmental Protection: Ensures that wastewater is treated to meet regulatory standards before being discharged or reused.
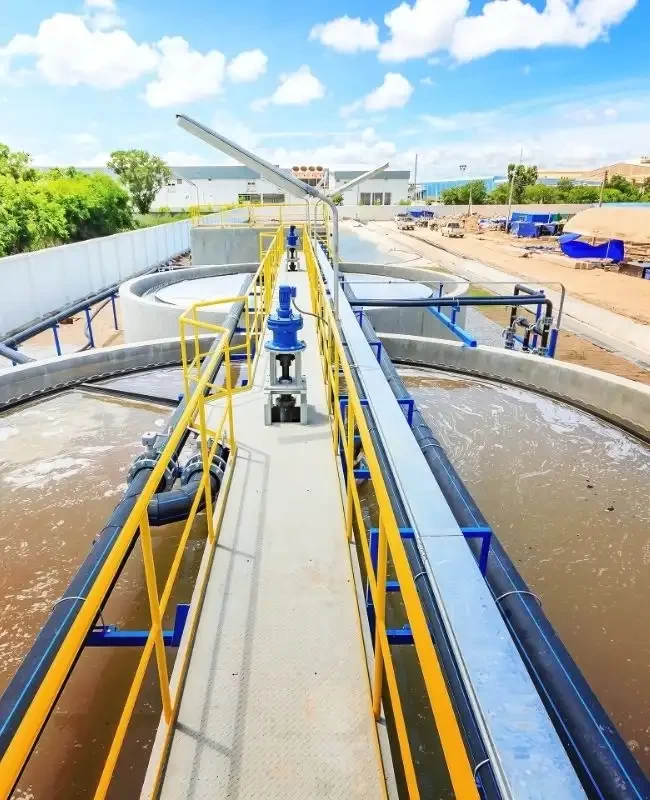

Products

Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)
Product Info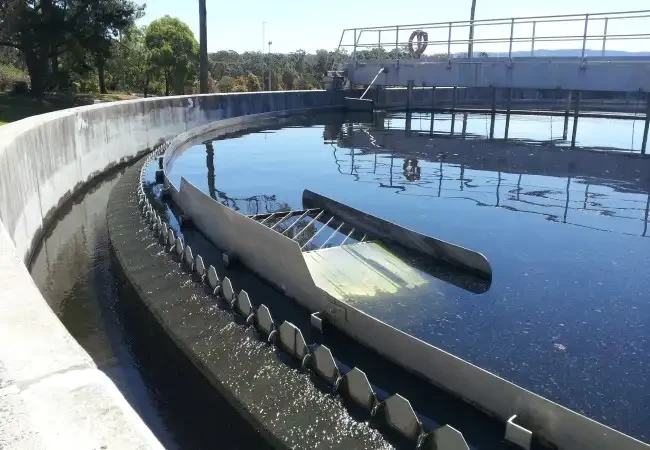
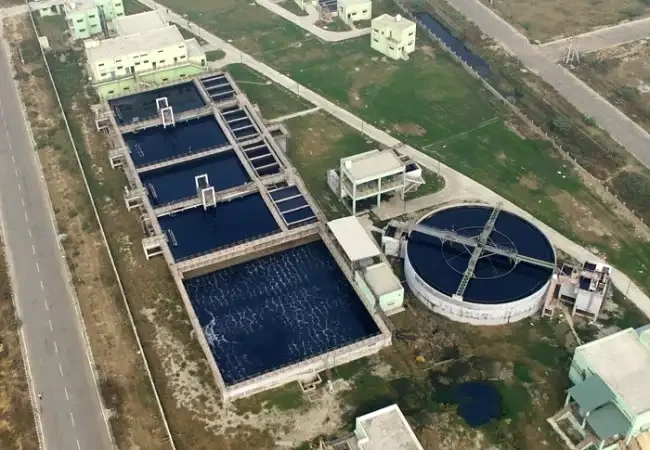
Effluent treatment Plant (ETP)
Product Info
Anaerobic Reactor (UASBR)
Product Info
DAF - Dissolved Air Flotation
Product Info
MBBR-Effluent treatment
Product Info
Membrane Bio Reactor
Product Info
Continuous Fill Batch Reactor
Product Info




